SPECT brain scan at leading private clinics.
Get your brain activity evaluated in just 20 minutes. Reveal mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) with an accurate 3-headed SPECT scanner.
What is SPECT?
A SPECT scan (single-photon emission computerized tomography) is used to look at the function of the organs. SPECT scanning of the brain is used to detect the areas where activity is too high or too low.
SPECT brain scan uses a radioactive substance, a special camera to catch the signals, and software to create 2D, and especially 3D, images of the brain. After the examination, the substance is out of the body after 3 hours, and the scan does not produce more radiation than a comprehensive X-ray examination.
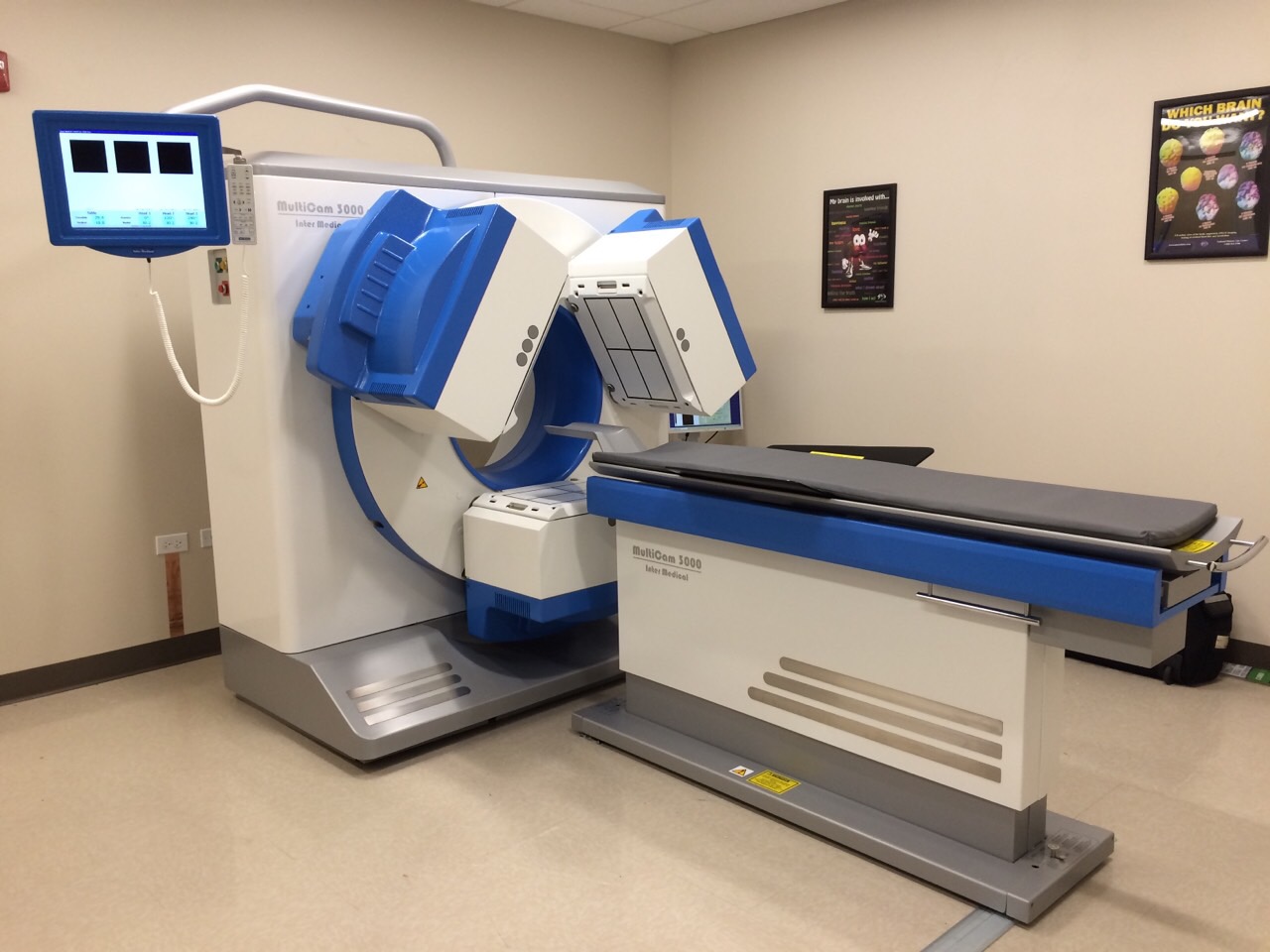
Photo: In a three-headed SPECT scanner, the scanning time is reduced to only 15-20 minutes. This makes it easier for children to lie still.
How does SPECT brain scan differ from the scans people know
SPECT scanning gives greater insight, especially in mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI) – insight not obtained with a symptomatic evaluation alone.
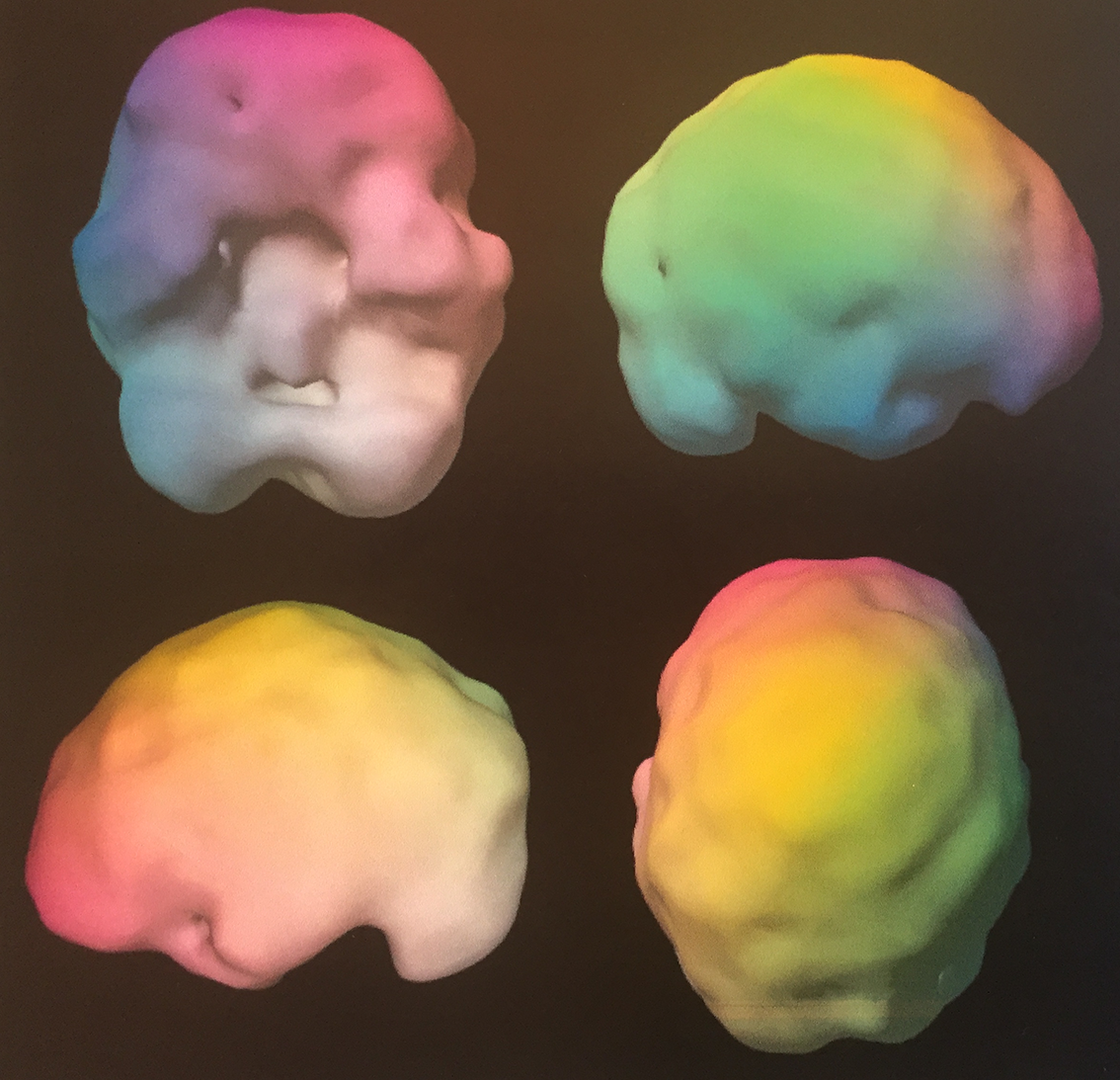
Where MRI and CT show physical structures inside the brain, a SPECT brain scan produces images that show the activity in different places in the brain. A SPECT scan of the brain reveals where there is local overactivity and underactivity (1a). It also shows how the blood flows in the brain.
A mild traumatic brain injury is seen as low activity locally in the injured area. Without SPECT, people can, after a concussion, be left without help or with the wrong help.
Figure: Injuries seen as low activity around the brainstem and left temporal lobe. SPECT scanning provides greater insight into minor brain trauma, insight that cannot be achieved with symptomatic evaluation alone.
Comment: The “holes” in the image of the brain are not physical holes. They are areas of the brain with low brain activity, measured as blood flow.
The most remarkable findings
with SPECT brain scans so far:
with SPECT brain scans so far:
SPECT brain scans can now be used to differentiate between relatively mild physical brain injuries (mTBI) and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Two research studies published in 2015 by researchers from UCLA and other places, examined a total of 20746 patients
and showed that the two conditions can be distinguished from each other with very high accuracy, by means of SPECT imaging. Read the articles (5a, 5b).
This achievement was recognized by Discover Magazine
as 19th out of the 100 best scientific news of 2015.
The study helps people with one or both of these conditions to get the right therapy.
Is SPECT experimental or evidence-based?
The days are over when SPECT is considered experimental.
- The Society of Nuclear Medicine and the European Association of Nuclear Medicine have recognized SPECT as a valuable diagnostic and prognostic tool for TBI (early concussion and chronic injury).
- The American College of Radiology recommends SPECT to diagnose symptomatic traumatic brain injury if no results are found after CT and/or MRI scans.
- A review has found evidence for the use of SPECT scanning for mild traumatic brain injury, mTBI (6).
In other words: SPECT scanning certainly works as a diagnostic tool for minor brain damage.
What to expect from a SPECT brain scan
You get two scans performed over two days in a private clinic, with a special agreement with benefits from REbrain Clinic,:
- A passive scan where you are almost asleep while you get a small amount of radioactive substance (tracer) in the bloodstream via a catheter
- An active scan where you do a digital “focus test” in a dark room while getting the tracer into the blood via a catheter
On the day of the scan, do not take food, supplements or medications that affect blood flow. No eating one hour before the scan. You get a practical guide.
The tracer is out of the body after 3½ hours.
SPECT scans are used to diagnose the following conditions:

- Traumatic brain injury, incl. mild Traumatic Brain Injury, mTBI (1)
- Thyroid problems
- PTSD (3a)
- ADD/ADHD /cognitive problems (3b)
- Anxiety
- Depression (3b, 3c)
- Disorders on the autism spectrum
- Early symptoms of Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia (3c)
- Other psychiatric illnesses
SPECT is also used for:
- Multiple sclerosis research
- Neurodegenerative disorders
- Other organ examinations
(However, not via the REbrain clinic)
SPECT Consensus
- Tatsch K, Asenbaum S, Bartenstein P, et al. European Association of Nuclear Medicine procedure guidelines for brain perfusion SPECT using (99m) Tc-labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002; (10): BP36-42.
- Positron Emission Tomography in Canada 2015. Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. https://www.cadth.ca/positron-emission-tomography-canada-2015.
- Injury prevention and control: traumatic brain injury. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.