People with chronic neck injury have symptoms of PCS
(post-concussion syndrome)
(post-concussion syndrome)
Symptoms of PCS
The symptoms of PCS, post concussive syndrome are:
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Irritability
- Dizziness
- Impaired memory
These symptoms are often reported in patients who have been diagnosed with mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) from sports concussions.
Are the symptoms from chronic neck injury the same as from mild traumatic brain injury/concussion?
Examination of PCS symptoms is used by doctors for the diagnosis of concussion /mild traumatic brain injury. But in fact, it is not entirely known whether the symptoms are 100% specific for mild traumatic brain injury …… or whether the PCS symptoms could possibly be due to concomitantly acquired neck-brain injury.
Patients ALSO often complain of several PCS symptoms after neck injuries such as whiplash, especially: headaches and neck pain.
In 2011-12, this led a group of Swedish researchers to examine a larger number of “chronically neck injured” for all symptoms of PCS (post concussion syndrome).
What% of chronic neck injuries have the classic symptoms of PCS /post concussion syndrome?
Results
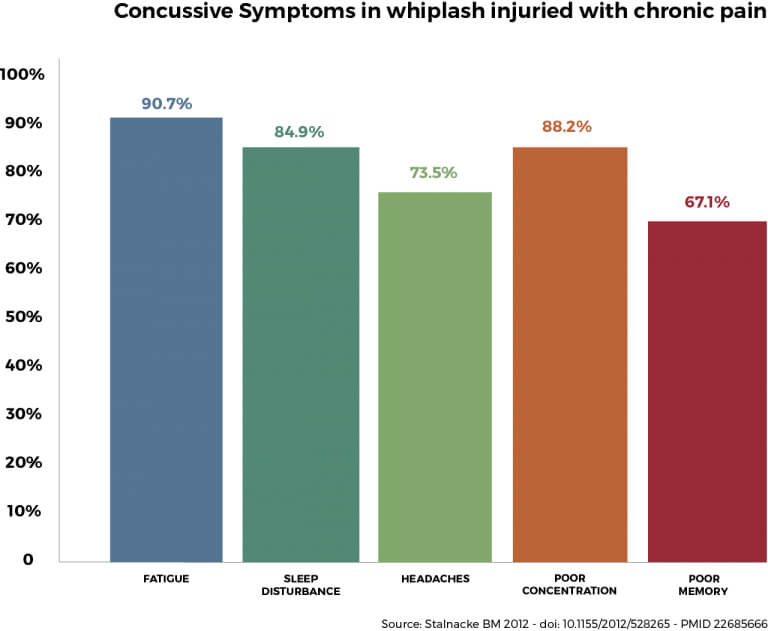
Fatigue (90.7%), sleep disturbance (84.9%), headaches (73.5%), poor concentration (88.2%) and poor memory (67.1%) were some of the most frequently reported PCS symptoms.
It was clear that almost everyone with chronic neck injury also has classic symptoms of chronic concussion/post concussion syndrome. Those with chronic neck injuries with PCS also suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression and anxiety, as is typically seen in people with chronic concussion.
What can we learn from the Swedish researchers?
To optimize the treatment of neck injuries, it is important
- To assess whether the chronically injured person also has a concussion/mild traumatic brain injury?
- One should look at the neck in people with concussion.
- REbrain Clinic argues for always scanning for neck and brain injury simultaneously in chronically injured. Then take action against both neck injury and brain injury to get rid of the symptoms.
- In addition to the physical injury mechanism, one should look at other factors, such as post-traumatic stress. If the physical injury was caused by an accident, one may have suffered a trauma. PTSD can therefore play a role alongside the physical injury. But that does not mean ignoring the physical injury!
- However, one should examine and treat depression and anxiety, as depression and anxiety are common in recurrent concussions, as a research study of NFL football players shows. NFL-fodboldspillere. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23709409/
REbrain Clinic helps with a broad solution
We help with that at REbrain Clinic.
We recommend that you have your neck thoroughly examined for physical injuries first, BOTH in the brain AND in the neck.
If you have a mental trauma behind you, no matter whenever in life it has happened, we recommend that you get it treated at the same time as your brain-neck injury. We take both equally seriously.
Comment
Mild traumatic brain injury, mTBI, is a minor injury after a concussion. mTBI has been thoroughly researched in the United States with functional MR scanning, fMRI. The big breakthrough came with the launch of the fMRI method 17 years ago.
Sources:
Stålnacke BM. Postconcussion symptoms in patients with injury-related chronic pain. Rehabil Res Pract. 2012;2012:528265. doi:10.1155/2012/528265. PubMed (hel artikel)
Amen DG, Taylor DV, Ojala K, Kaur J, Willeumier K. Effects of brain-directed nutrients on cerebral blood flow and neuropsychological testing: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. Adv Mind Body Med. 2013;27(2):24-33. PubMed